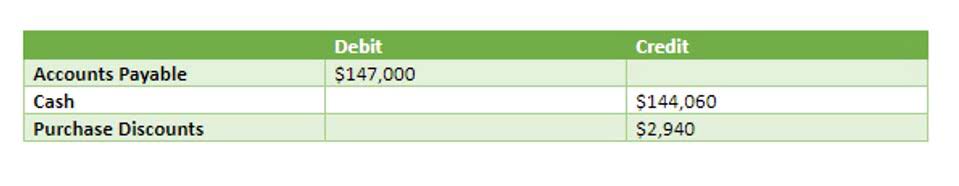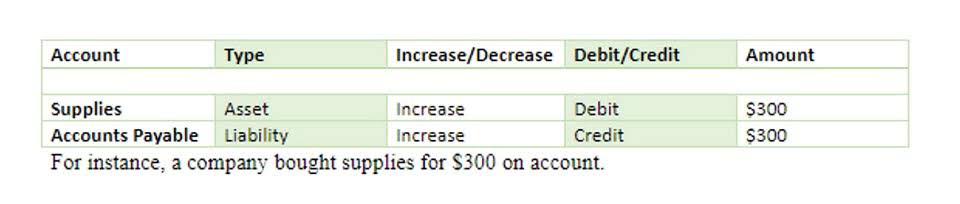
Despite some calls to modernize, MM persists because of its advantages for clarity, precision, and familiarity. After analyzing its history and modern use, I have a new appreciation for how deeply rooted MM is within finance culture, likely to endure for the foreseeable future. To understand MM, we have to go back to the early mm finance meaning days of accounting when Roman numerals were used to record ledgers. Therefore, understanding and using this term is crucial in the field of finance. Large numbers can be difficult to comprehend and interpret correctly, thus using MM to represent millions simplifies presentations and discussions, making them more efficient.
Why Is It Called the Money Market?
- Money market funds, foreign banks, and large corporations invest in them because they pay a slightly higher interest rate than U.S. government debt.
- Quite frankly, it’s what keeps your company afloat; an organization can’t operate successfully if it’s not financially sound.
- During the decade spanning from 2000 to 2010, the monetary policies of the Federal Reserve Bank led to short-term interest rates—the rates banks pay to borrow money from one another—hovering around 0%.
- Understanding the financial implications of your decisions and clearly communicating those decisions to key stakeholders can help advance your career.
- The use of “MM” fit seamlessly into this new framework, offering a concise way to represent substantial amounts without cluttering financial records.
It involves overnight swaps of vast amounts of money between banks and the U.S. government. The majority of money market transactions are wholesale transactions that take place between financial institutions and companies. Orange Financial LLC is a firm that provides financial services to both companies and individuals. This account offers a return on investment a little bit higher than what the regular savings account is currently offering.

Share this Article
Furthermore, using MM can make a large-scale monetary value easier to quickly grasp, both visually and conceptually, as it simplifies the financial quantities being discussed or presented. In financial operations – where every zero in a number is crucial – abbreviating large figures helps reduce potential errors when handling complex calculations and transactions. The term enables clarity and consistency, reducing the risk of misunderstandings due to different interpretations of number notation. In various aspects of finance such as budgeting, financial analysis, reporting, and forecasting, the use of MM aids in ensuring accuracy and precision. The least ambiguous approach is to simply write them out in words, such as “$ thousands.” This is CFI’s recommended method, to avoid any potential confusion. As one discovers from the many variant opinions this topic generates significant misunderstanding.
How was the mm abbreviation created?
The term “MM” originates from the Roman numeral M, which stands for one thousand. It is commonly used in financial documents, accounting, and stock market where space is a concern. The term MM is used in the finance world to denote one million and is a standard nomenclature used across the globe.
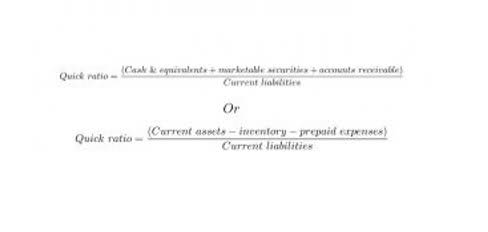
Money Markets vs. Capital Markets
- If K and MM are used, it’s bad style because the symbols are being mixed up.
- This convention originated from Roman numeral accounting traditions and became engrained centuries ago.
- “M” is derived from the Roman numeral for 1,000, and it is often used to denote thousands.
- The commercial paper market is for buying and selling unsecured loans for corporations in need of a short-term cash infusion.
- The use of “MM” became more entrenched as these standards aimed to harmonize financial reporting across different jurisdictions, ensuring consistency and comparability.
The theorem was developed in the 1950s by Merton Miller and Franco Modigliani. One of the primary benefits of using “MM” in international reporting is its ability to reduce ambiguity. Financial documents often traverse multiple jurisdictions, each with its own set of conventions and terminologies.
Please review the Program Policies page for more details on refunds and deferrals. We accept payments via credit card, wire transfer, Western Union, and (when available) bank loan. Some candidates may qualify for scholarships or financial aid, which will be credited against the Program Fee once eligibility is determined. Please refer to the Payment & Financial Aid page for further information. Our easy online application is free, and no special documentation is required. All participants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the program.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Money Markets
- Money market funds appear attractive to investors as they come with no loads (no entry or exit charges).
- Retail money funds are accessible to individual investors as a result of their small minimums.
- Any excess earnings generated through interest on the portfolio holdings are distributed to the investors as dividend payments.
- Some of those wholesale transactions eventually make their way into the hands of consumers as components of money market mutual funds and other investments.
- M&M challenged the belief that debt was cheaper than equity and that companies could strive for an optimal capital structure.